Sport (Level 2 and 3 BTEC)

Subject Vision
Adventure – Students will have the opportunity to explore different types and providers of sport and physical activity. Learn about physical fitness and outdoor adventure and their benefits. Undertake practical sessions to develop skills in planning and delivering sports activity sessions to participants. The qualification enables students to take risks, develop their sector-specific skills, such as sport analysis and sports leadership, using realistic vocational contexts, and personal skills, such as communication, planning, time management and teamwork through a practical and skills-based approach to learning and assessment.
Resilience – We strive to push all students to achieve their personal best, and demonstrate the importance of correct technique in order to master skill and fulfil their personal goals.
We want our students to recognize the importance of having high aspirations and aim to ensure that all students have the ability to manage their emotions and achieve the best grades throughout their PSA tasks
Independence – When completing PSA tasks for component 1 and 2, students have the opportunity to take ownership of their learning and know how and when to seek support.
Challenge – –All activities challenge students to become effective decision makers, build character and achieve their personal best. Component 1 and 2 provides students with the opportunity to have the confidence to challenge themselves when deliver a warm up and coaching sessions.
Curiosity – They will also explore the different types of participant and their needs in order to gain an understanding of how to increase participation for others in sport and physical activity and further develop their knowledge and understanding of anatomy and physiology
Throughout the BTEC Sport curriculum, students have the opportunity to investigate the components of fitness and their effect on performance, take part in practical sport, explore the role of officials in sport and learn to apply methods and sporting drills to improve other participants’ sporting performance.
Community – When studying component 1, students have the opportunity to look at local sporting provision within our community. From taking part in practical activities students develop respect and care for each other and the wider environment.
Staff
Homework
Year 10
10 A Sport - Wednesday
10 B Sport - Thursday
10C Sport – Wednesday
Year 12
To use the revision resources on the school website in Revision Key stage 5 and learn the topice completed each week.
Our Learning Journey
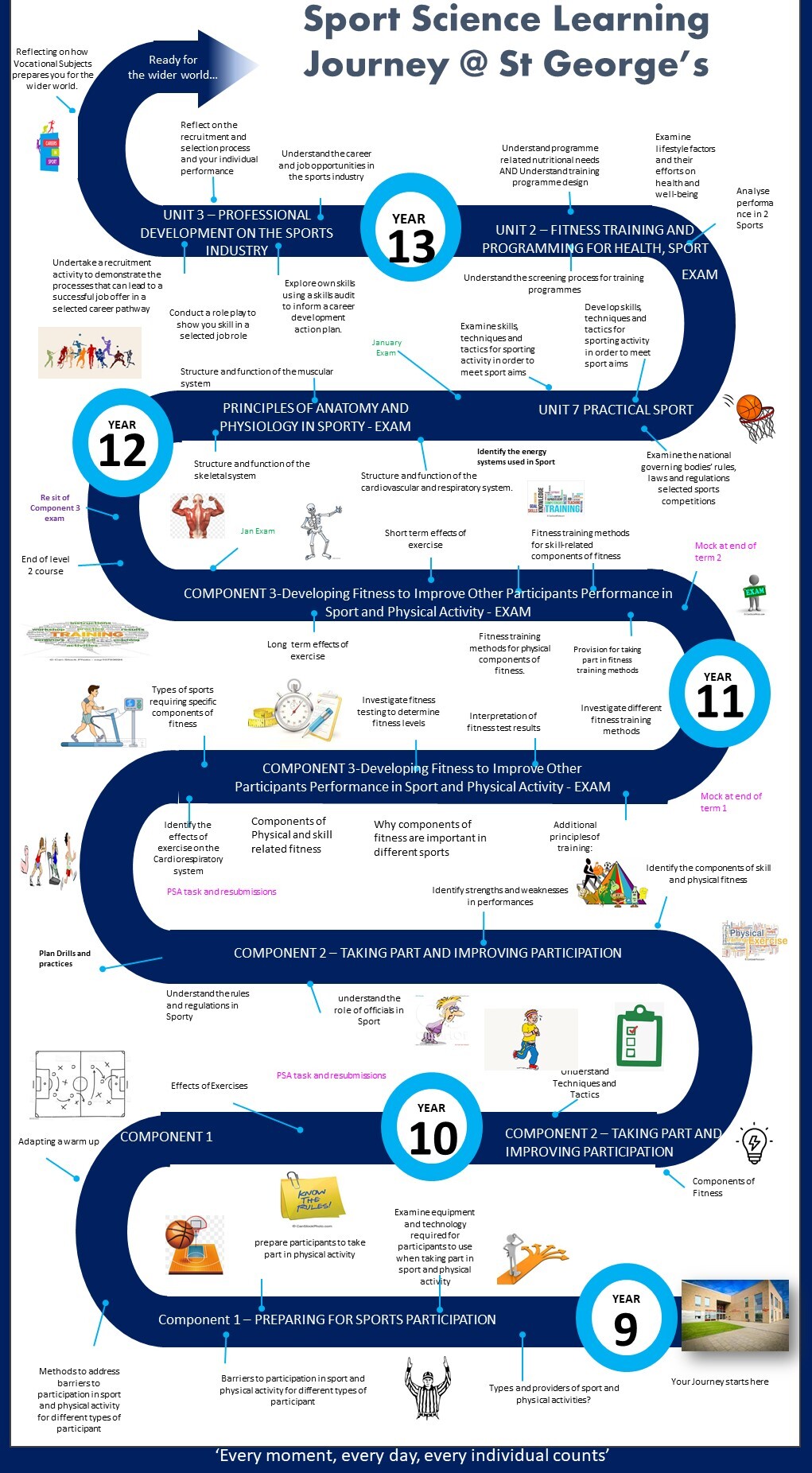
Level 2 Subject Information - KS4
BTEC Level 1/2 Tech Award (2022)
| Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 | Term 4 | Term 5 | Term 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 9 | Component 1 - LA C and LA A | |||||
| Year 10 |
Component 1 - Learning Aim A & B Non Examined Assessment PSA |
Component 1 = Non Examined Assessment PSA |
Component 2 - Learning Aim A |
Component 2 = Non Examined Assessment PSA |
Component 2 = Non Examined Assessment PSA |
Component 3 = Exam Prep |
| Year 11 |
Component 3 = Exam Prep |
Component 3 = Exam Prep |
Component 3 = Exam |
Resit |
Resit |
Revision - BTEC Level 2 Tech Award (KS4)
GENERAL INFORMATION (USEFUL INFORMATION FOR PARENTS)
Component 1 and 2 are taught in Year 10
Component 3 are taught in Year 11
| Personal Learning Checklist | |
|---|---|
| Example Exam Questions/Model Answers | |
| Revision Materials/Sharepoint |
Sharepoint Revision - click here (Pupils must log in with their username as their usual computer login followed by @st-georgescofe-thanet.kent.sch.uk (e.g. JSmith123@st-georgescofe-thanet.kent.sch.uk) and their usual password they use to log on to school laptops) |
| Revision Guide |
Pearson Revise BTEC Tech Award Sport Revision Guide (2022) - £6.49 ISBN:9781292436142 |
Revision - BTEC Level 3 National (KS5)
GENERAL INFORMATION (USEFUL INFORMATION FOR PARENTS)
Course book are extremely useful for the 4 units that are delivered across the two years - Click Here
- Unit 1 and 7 are taught in year 12 across 5 hours a week.
- Unit 2 and 3 are taught in year 13 across 5 hours a week
- Unit 1 and 2 have an exam, while unit 3 and 7 are course work units.
Specification can be found here
Free sample of the student book: preparing for assessment (unit 1) - Click Here
| Personal Learning Checklist |
Unit 1 = Click Here Unit 2 = Click Here |
|---|---|
| Example Exam Questions/Model Answers |
Unit 1 June 2017 - Click Here June 2018 - Click Here January 2020 - Click Here Examiners report = Summer 2019 - Click Here Unit 2 January 2018 - Click Here Examiners report = Summer 2019 - Click Here |
Revision Material/Sharepoint
Revision Guide - Energy Systems
Revision Guide - Muscular System
Revision Guide - Respiratory System
Revision Guide - Skeletal System
Revision Guide
(Pupils must log in with their username as their usual computer login followed by @st-georgescofe-thanet.kent.sch.uk (e.g. JSmith123@st-georgescofe-thanet.kent.sch.uk) and their usual password they use to log on to school laptops)
Job Opportunities / Careers
TYPES OF CAREERS IN THE SPORT INDUSTRY
The physical fitness and good teamwork which come from an interest in physical education and playing sports can be useful in many different careers including leisure, sport and tourism, construction, education and training, armed forces, security and uniformed services, management, as well as animals, agriculture, plants and land.
Applied and job-related learning
There is a range of vocational qualifications (such as BTECs, NVQ/SVQs and diplomas) linked to physical education and sport, including:
- sports and exercise science
- sport
- business, personal training and sports massage
- travel and tourism
- outdoor leisure
- uniformed public services
Apprenticeships
There are a range of apprenticeships associated with an interest in PE and sport such as:
- leisure centre assistant
- gym instructor
- PE and school sport coach
- fitness instructor
- personal trainer
- life guard
PERSONAL TRAINER
What does a personal trainer do?
Personal trainers talk to clients to find out about their fitness level and health history. They would then:
- set realistic short-term and long-term goals and plan programmes for reaching them
- educate, motivate and coach clients to help them follow their programmes safely and effectively
- give clients advice on health, nutrition and lifestyle changes
- help clients with their workouts
- check and record clients' progress, using methods such as measuring heart rate and body-fat levels
In some cases you might work full-time as a gym instructor and do personal training outside your normal hours of work.
What do I need to do to become a personal trainer?
To become a personal trainer you would normally be an experienced fitness instructor with a recognised qualification, such as:
- Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing – Gym
- Level 2 Diploma in Health, Fitness, and Exercise Instruction
- Level 2 Diploma in Instructing Exercise and Fitness
You can take further qualifications specific to this career, which include:
- Level 3 Diploma in Fitness Instructing and Personal Training
- Level 3 Diploma in Personal Training
Fitness instructor and personal trainer courses are widely available through colleges and private training providers.
Membership of a professional organisation, such as the Register of Exercise Professionals (REPs) or National Register of Personal Trainers (NRPT) is also a good way to demonstrate your competence and skills and can help to improve your career prospects.
If you are already a qualified fitness instructor, you could take the Level 3 Award in Conversion of Advanced Fitness Instructor to Personal Trainer Status. This allows you to change your membership status on the REPs to Personal Trainer.
To work as a personal trainer you must also have public liability insurance and a first aid award. This must include a cardio-pulmonary resuscitation certificate (CPR). Professional bodies can advise on this as well as tax, insurance and self-employment issues.
Related skills
- Interpersonal skills
- Organisation
- Patience
Vocational route
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing – Gym
Level 2 Diploma in Health, Fitness, and Exercise Instruction
Level 2 Diploma in Instructing Exercise and Fitness
Level 3 Diploma in Fitness Instructing and Personal Training
Level 3 Diploma in Personal Training
Where to find out more
PHYSICAL EDUCATION TEACHER
What does a secondary school teacher do?
Secondary school teachers teach children from the ages of 11 to 18. You will plan lessons and assess work based on standards set out in the curriculum (England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland all have their own specific curriculum requirements). Communication skills and excellent literacy and numeracy skills are essential for this role
What do I need to do to become a secondary school teacher?
To teach in a UK state school, you will need to a have a degree, and a recognised teaching qualification. There are a number of routes you can take to become a secondary school teacher.
You could follow an undergraduate Initial Teacher Education or Training (ITET) programme, such as a Bachelor of Education (BEd) degree. This is generally a popular route for prospective primary school teachers, but some universities do offer secondary-level BEd programmes for some specialisms.
Alternatively, you could do a degree – this could be in a subject you wish to specialise in like maths, science, or English – then take a postgraduate teacher training programme, such as a PGCE or PGDE. You must have a degree in the subject you have chosen to teach (or a closely related one).
To get into university, you will need to have completed courses like GCSEs, Nationals, A levels, Highers, the International Baccalaureate, or Cambridge Pre-Us. You will also need to pass a police criminal records, or Disclosure and Barring Service (DBS), check
Related skills
- Communication
- Creativity
- Discipline
- Interpersonal skills
- IT
- Leadership
- Literacy
- Numeracy
- Organisation
- Patience
- Problem solving
- Teamwork
- Time management
Essential qualifications
- Undergraduate education degree
- OR undergraduate degree AND a PGCE/PGDE
- DBS or police records check
SPORTS COACH
What does a sports coach do?
Sports coaches train and coach amateur and professional athletes. You could be working one-on-one with an individual in sports like tennis, gymnastics or boxing, or you could be working with a group of people like a football, netball or rugby team.
As a sports coach, you’ll ensure the physical and mental wellbeing of the athletes you work with. You’ll make sure they can perform to the best of their abilities in competitions. You’ll need to be physically fit and understand all the rules of your chosen sport.
What do I need to do to become a sports coach?
To become a sports coach, you will need to have a coaching qualification that is recognised by the governing body for your sport.
If you're interested in taking a higher education qualification in sports science it would be helpful to take a science-related subject at A level. Check entry requirements with universities.
Relevant level 3 vocational courses (eg BTEC National Diploma science or sports and exercise science) are acceptable for some sports science degrees. Check with universities.
Related skills
- Teamwork
- Physical fitness
- People management
- Communication
- Leadership
Essential qualifications
- Coaching qualification (see the website for the governing body of your sport for details)
Desirable qualifications
- Sports science degree
Sports Nutritionist/dietician
Salary: £20,000 to £35,000 +
Job role
As a nutritionist, you'll generate, assess and deliver scientific evidence-based nutritional advice in a variety of settings to improve health and wellbeing and to promote a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Qualification & development requirement:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s a grade 4 in Maths, English, Science’s and Sport
A-level/BTEC Sport science and biology preferably
Undergraduate degree in BSc Sport & Exercise Science or Sports Nutrition based degree
Registration to the associate nutritionist or The British Dietetic Association.
Further development is via a master degree or PHD in nutrition.
PE Teacher
Salary: £23,720 to £35,008 +
Job role
Physical education teacher’s help children develop physical abilities and healthy habits that can last for the rest of their lives.
Qualification & development requirement:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 in English, Maths, Science & Sport.
A-level/BTEC: Sport & preferably biology.
Undergraduate degree: BSc Physical education, Sport & exercise science or any other sport science related degree.
Postgraduate degree: PGCE Secondary physical education via university, schools direct or a scitt program.
Other qualifications and experiences: Coaching level 1 & 2 badges and multiple sports is advantageous. In addition having work experience within a school setting.
Physician Associate
Salary: £27,000 to £35,000 +
Job role
You'll hold a variety of responsibilities and will typically work in general practitioner (GP) surgeries or hospitals as part of a medical team.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science (Preferably Biology) & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Grade 4 Science, Biology & Sport science
Undergraduate degree: a life science-related degree and/or to be a registered healthcare professional, such as a nurse.
Postgraduate degree: MSc Physician associate studies
Experience: Preferably experience working has a healthcare assistant or with St Johns ambulance.
Sport Scientist
Salary: £20,000 to £30,000 +
Job role
Sports science focuses on improving athletic performances through the applications of psychology, physiology and biomechanics principles and techniques. Sports scientists observe and monitor athletes to design performance-improving exercise and training programs.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Sport science and preferably biology
Undergraduate degree: BSc Sport & exercise science
Experience: Preferably experience working with a sports clubs has a volunteer video analysis
Exercise physiologist
Salary: £23,023 to £35,000 +
Job role:
As an exercise physiologist you'll investigate how people respond and adapt to muscular activity and will use your skills and knowledge to improve their performance and fitness levels or to help prevent or treat illness.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Sport science or preferably biology
Undergraduate degree: Sport & exercise science or other sport science based degree
Postgraduate degree: MSc Clinical Exercise Physiology
Experience: Preferably working within the laboratory setting voluntary or NHS.
Physiotherapist
Salary: £23,023 to £36,644 +
Job role:
Helps to restore movement and function when someone is affected by injury, illness or disability. It can also help to reduce your risk of injury or illness in the future. It takes a holistic approach that involves the patient directly in their own care.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Sport Science
Undergraduate degree: BSc Physiotherapy
Postgraduate degree: A master’s degree is optional but must be approved by the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC). This will make you eligible for a membership of the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy (CSP)
Sports psychologist
Salary: £27,000 to £37,000 +
Job role:
Helping athletes and other sports people to use psychological principles to achieve optimal mental health and to improve performance on the field.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Sport Science
Undergraduate degree: BSc Psychology or Sport Psychology based degree
Postgraduate degree: Conversion courses on to Psychology are available. In addition all undergraduate and master degree must meet the standard of the British Psychological Society.
Experience: Preferably volunteering with a sport psychologist of consultancy, school setting or internships.
Sports coach
Salary: £15,000 to £35,000 +
Job role:
Sports coaches assist athletes in developing to their full potential. They are responsible for training athletes in a sport by analysing their performances, instructing in relevant skills and by providing encouragement. But you are also responsible for the guidance of the athlete in life and their chosen sport.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & Sport.
A-level/BTEC: Sport
Undergraduate: BSc Sport science and coaching (optional)
Experience: Local clubs & schools. In addition Level 1 & 2 coaching certificates of chosen sport are necessary.
Personal trainer
Salary: £16,000 to £30,000 +
Job role:
A personal trainer creates one-on-one fitness programmes for their clients, motivating and guiding them to achieve their goals. Clients may wish to lose weight or gain muscle, and as a personal trainer you'll teach and help them to exercise properly using workouts and specific plans. You'll instruct and advise your clients, using a range of fitness machines, classes or weights.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 English, Maths, Science & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Level 3 personal training qualification, ideally one accredited by a reputable organisation such as the Register of Exercise Professionals (REPS) or the Chartered Institute for the Management of Sport and Physical Activity (CIMSPA).
Undergraduate degree: It's not necessary to have a degree to be a personal trainer. However, if you do wish to undertake a higher education qualification you should choose BSc Sport science and personal training.
Strength and conditioning coach
Salary: £17,100 to £38,000 +
Job role
Strength and conditioning coaches usually provide exercise counselling to athletes so they may improve their strength, speed, and endurance.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & Sport
A-level/BTEC: Sport Science
Undergraduate degree: Preferably BSc Strength and conditioning or other sport science based degrees.
Postgraduate degree: MSc Strength and conditioning. In addition must be UKSCA Accredited.
Experience: Voluntary experience working with locals teams, clubs and individual athletes
Sports Medicine/Physician
Salary: £25,000 to £40,000 onwards
Job role:
Diagnose, treat, and help prevent injuries that occur during sporting events, athletic training, and physical activities.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science, Sport & Biology
A-level/BTEC: Sport (preferably Science or Biology)
Undergraduate degree: BSc Sport & Exercise Science or Sports Medicine
Postgraduate degree: MSc Sports Medicine
Sports agent
Salary: £24,876 to £34,537 +
Job role:
Sports Agents handle all aspects of an athlete’s career, helping to secure and negotiate contracts, and look after their client’s personal and professional interests.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 Maths, English, Science & preferable Sport and Business
A-level/BTEC: Business Studies and Sport Science
Undergraduate degree: BA Sports management or any other sport business/ marketing related degree.
Sport journalist
Salary: £24,250 to £40,000 +
Job role:
Writing that reports on sporting topics and competitions. Sports journalism is the essential element of many news media organizations.
Qualification & development requirements:
GCSE’s/BTEC’s: Grade 4 English, Maths & Science Preferably Media, Journalism and Sport
A-level/BTEC: English, Sport & media (Apprenticeships are available via the BBC)
Undergraduate degree: BSc Sports journalism or any journalism based degree
Experience: Working or volunteering for local new papers, radio stations or independent journalism.


